“God mode”, for those who aren’t gamers, is a mode of operation (or cheat) built into some types of games based around shooting things. In God mode you are invulnerable to damage and you never run out of ammunition.
GAO Report on Emerging Pentagon Battle Management Programs
GAO Report on Emerging Pentagon Battle Management Programs
GAO Report on Emerging Pentagon Battle Management Programs
The following is the January 2023 Government Accountability Office report, Battle Management DOD and Air Force Continue to Define Joint Command and Control Efforts.
What GAO Found
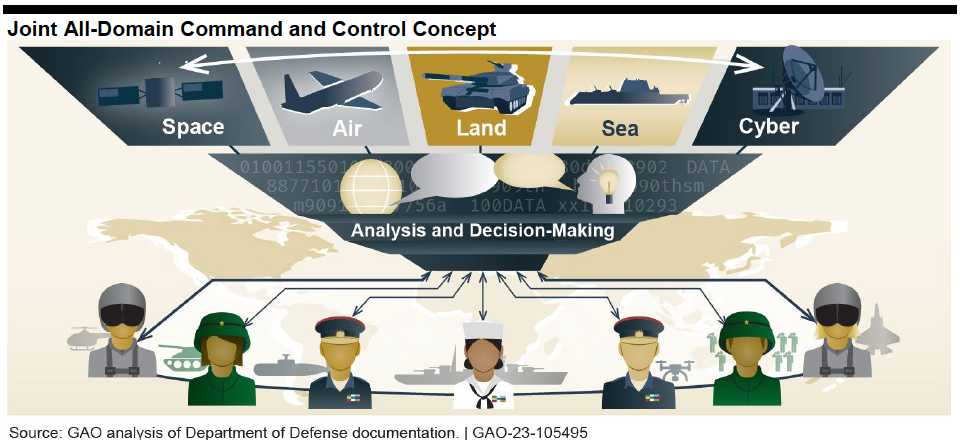
Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) is a long-term effort to connect military assets across space, air, land, sea, and cyber domains. The Department of Defense (DOD) intends for JADC2 to analyze warfighting data across all of those domains to allow decision makers to identify, execute, and monitor operations more effectively.
DOD is in the early stages of developing JADC2 and released initial guidance, including a strategy that outlines broad goals. However, DOD has not yet defined the details, such as which existing systems will contribute to JADC2 and what future capabilities need to be developed. A House report directed DOD to report on the scope, cost, and schedule of the overall JADC2 effort. Currently, DOD is in the early stages of determining those elements.
In April 2020, GAO reported on the Air Force’s contribution to JADC2—the Advanced Battle Management System (ABMS)—and recommended that the Air Force develop acquisition and planning documents. Since then, the Air Force has taken steps to do so and has defined two ABMS efforts:
- Capability Release 1 intends, in part, to enable F-35 data connectivity with command and control centers, and the Air Force plans to deliver prototypes in 2024. This is a shift from original Capability Release 1 plans, which also included F-22 data connectivity. The Air Force intends to update documents to reflect this change.
- Cloud-Based Command and Control intends to integrate a variety of air defense data sources to support homeland defense. The Air Force plans to deliver initial capabilities in 2023; however, it is in the process of identifying those capabilities.
In June 2022, the Air Force established a consortium of companies to assist in developing requirements for a network, called the ABMS Digital Infrastructure, to enable ABMS efforts. Additionally, in September 2022, the Air Force established a new leadership structure for ABMS. While these are positive steps toward developing ABMS, the Air Force has not delivered any capabilities to date and is in the process of identifying future capabilities and when they will be delivered.
Why GAO Did This Study
DOD military commanders require a real-time, complete picture of the battlespace to quickly make informed decisions. Historically, DOD has prioritized individual systems over joint capabilities and interoperability. DOD intends for JADC2 to address this issue by connecting warfighting capabilities through digital networks to enable commanders to effectively communicate and share information. Each military department is contributing to JADC2; the Air Force’s part is called ABMS.
Members of Congress included a provision for GAO to conduct a review of ABMS. In addition, GAO was asked to evaluate how ABMS will contribute to DOD’s broader goals for JADC2. This report addresses the extent to which (1) DOD has defined JADC2, and (2) the Air Force has developed plans for ABMS.
GAO reviewed planning and acquisition documents for JADC2 and ABMS, JADC2 implementation guidance, and ABMS contracts, among other documents. GAO also interviewed officials from the Joint Staff, Office of the Secretary of Defense, Air Force (including ABMS leadership), Space Force, Navy, Marine Corps, and Army.
What GAO Recommends
In April 2020, GAO recommended the Air Force develop a plan to mature technologies, develop a cost estimate, and conduct an affordability analysis for ABMS. DOD concurred. The Air Force is taking steps to address the recommendations—through acquisition and planning documents—but needs to do more to fully address them.
Republished in the State of California as a work of the United States government.

The Government Accountability Office, the audit, evaluation, and investigative arm of Congress, exists to support Congress in meeting its constitutional responsibilities and to help improve the performance and accountability of the federal government for the American people. GAO examines the use of public funds; evaluates federal programs and policies; and provides analyses, recommendations, and other assistance to help Congress make informed oversight, policy, and funding decisions. GAO’s commitment to good government is reflected in its core values of accountability, integrity, and reliability.
Related Articles
Understanding the building blocks for Australia’s quantum future
Australia is undergoing an exciting period of strategic technology policy review and development. The release of its first National Quantum Strategy this week committed the government to building the world’s first error-corrected quantum computer. This is a strategically important technology that has the potential to improve productivity and supply chain efficiency in diverse industries, lower costs across the economy, help reduce carbon emissions and improve public transportation.
Japan needs stronger deterrence than its new defense strategy signals
Since World War II, Japan had long chosen not to possess long-range strike capabilities that could be used against enemy bases. But the Japanese government changed course in December 2022 when it adopted the new national defense strategy (NDS), which included a commitment to acquiring a so-called counterstrike capability. But in order for this new strategy to contribute to deterrence and alter the nation’s defensive role as the ‘shield’ in its alliance with the United States, Tokyo needs to go further than what the NDS outlines.